Archives
- 2026-01
- 2025-12
- 2025-11
- 2025-10
- 2025-09
- 2025-03
- 2025-02
- 2025-01
- 2024-12
- 2024-11
- 2024-10
- 2024-09
- 2024-08
- 2024-07
- 2024-06
- 2024-05
- 2024-04
- 2024-03
- 2024-02
- 2024-01
- 2023-12
- 2023-11
- 2023-10
- 2023-09
- 2023-08
- 2023-07
- 2023-06
- 2023-05
- 2023-04
- 2023-03
- 2023-02
- 2023-01
- 2022-12
- 2022-11
- 2022-10
- 2022-09
- 2022-08
- 2022-07
- 2022-06
- 2022-05
- 2022-04
- 2022-03
- 2022-02
- 2022-01
- 2021-12
- 2021-11
- 2021-10
- 2021-09
- 2021-08
- 2021-07
- 2021-06
- 2021-05
- 2021-04
- 2021-03
- 2021-02
- 2021-01
- 2020-12
- 2020-11
- 2020-10
- 2020-09
- 2020-08
- 2020-07
- 2020-06
- 2020-05
- 2020-04
- 2020-03
- 2020-02
- 2020-01
- 2019-12
- 2019-11
- 2019-10
- 2019-09
- 2019-08
- 2019-07
- 2019-06
- 2019-05
- 2019-04
- 2018-07
-
br Materials and methods br Results br
2021-04-06
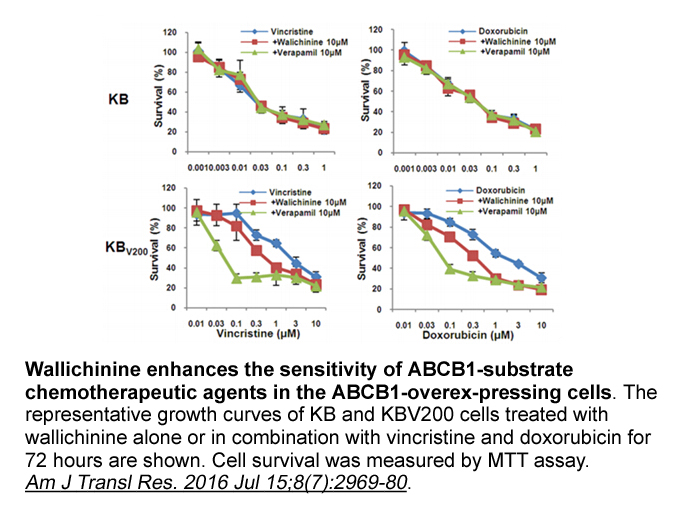
Materials and methods Results Discussion In general, CI symptoms are often visible only after the chilled products have been removed from coolstore to a warmer temperature (Schirra and Cohen, 1999). However, in the present work, 'satsuma’ mandarin fruit stored at 2°C showed chilling symptom
-
Cell Counting Kit-8 The IP R is a ubiquitously expressed
2021-04-06
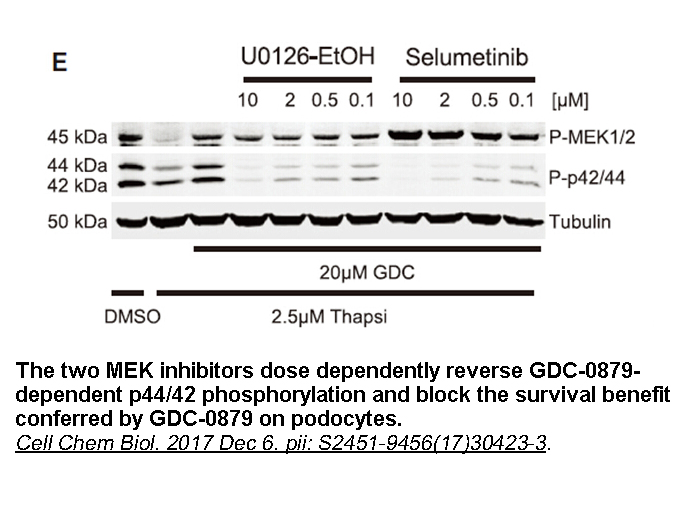
The IP3R is a ubiquitously expressed Ca2+-release channel from the ER, activated by IP3, produced upon cellular stimulation by hormones, growth factors or neurotransmitters. Three genes are coding for the IP3R and their gene products (IP3R1, IP3R2, IP3R3) assemble in functional homo- or heterotetram
-
Atg cleaves Atg at the peptide bond on
2021-04-06
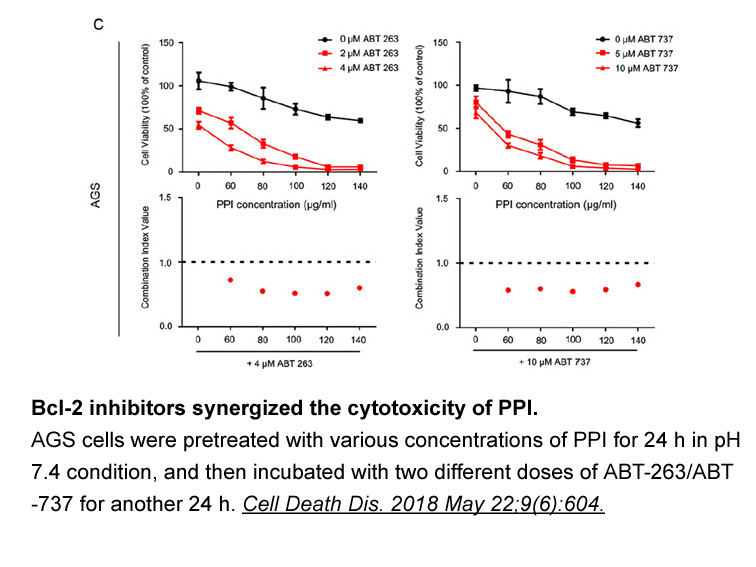
Atg4 cleaves Atg8 at the peptide bond on the glycine residue at the C-terminus, thus allowing the conjugation of Atg8 to phosphatidylethanolamine (PE) with the participation of other autophagy molecules. Atg4 can also serve as a deconjugating enzyme, which cleaves the amide bond of the conjugated At
-
Recent data obtained with etifoxine suggest that facilitatio
2021-04-06
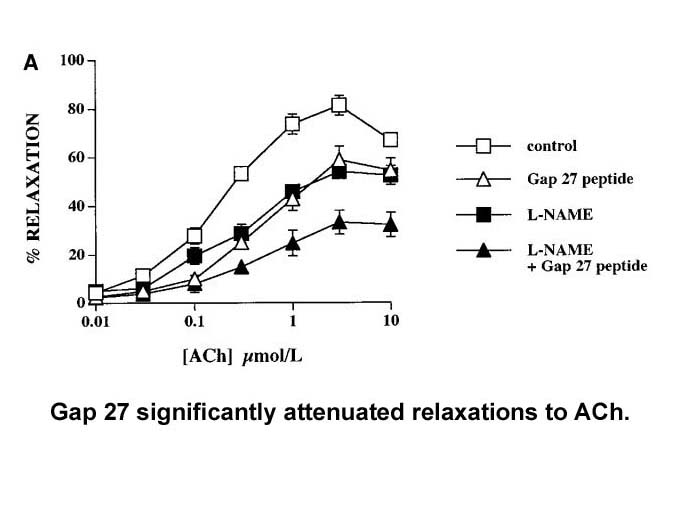
Recent data obtained with etifoxine suggest that facilitation of GABAergic inhibition may be also associated with an indirect mechanism implying activation of the peripheral benzodiazepine receptor with a subsequent increase in neurosteroid production (Schlichter et al., 2000, Verleye et al., 2005).
-
Within their range of applicability
2021-04-06
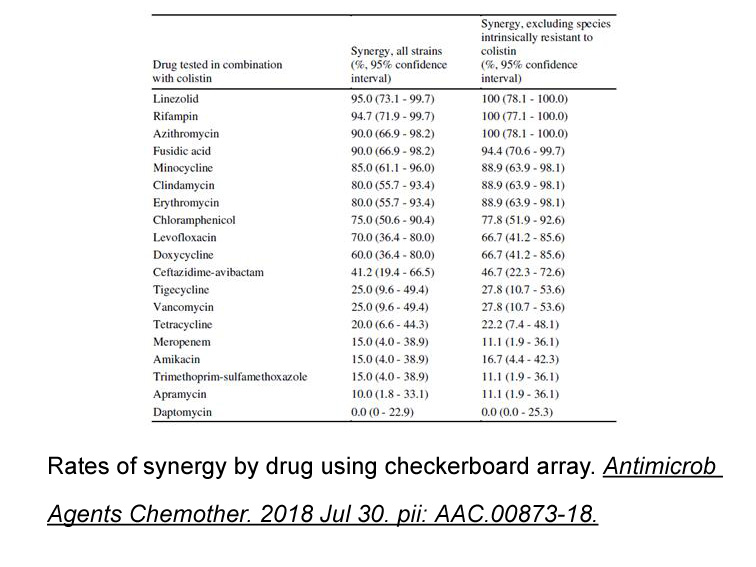
Within their range of applicability, both approaches matched the phase boundaries and yields generally to within the measurement error. The approaches matched the phase compositions generally to within 11 wt% or less with the average absolute deviations listed below: One advantage of the proposed
-
Ac-IETD-AFC br Introduction The endeavor to achieve a succes
2021-04-06
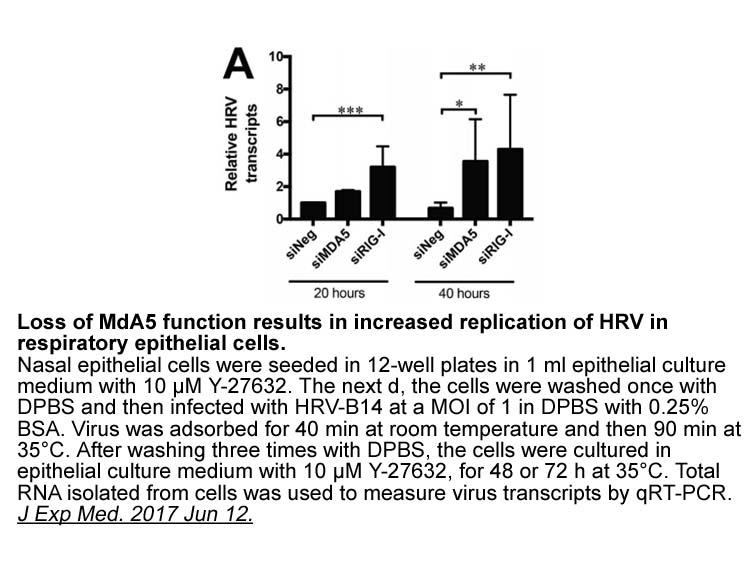
Introduction The endeavor to achieve a successful use of commercial-off-the-shelf (COTS) electronic devices in space is not new and the reasons are well known [1], [2], [3]. More recently, COTS have been widely employed in the manufacturing of low-cost, small satellites, for scientific and even c
-
Over the last decade numerous studies have evaluated
2021-04-02
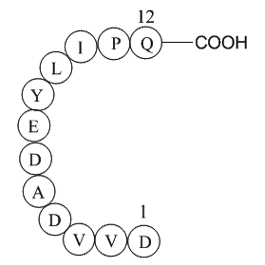
Over the last decade, numerous studies have evaluated the acute, short-term, and medium-term impact of pulmonary vasodilators on Fontan physiology.23., 24., 25., 26., 27., 28., 29., 30., 31. Although different Amadacycline synthesis of medications have been evaluated, phosphodiesterase-5 (PDE-5) in
-
Previous studies in the Swiss Webster mouse Rosengren
2021-04-02

Previous studies in the Swiss Webster mouse (Rosengren et al., 1995) and the Sprague–Dawley rat (El Sisi et al., 1993) have shown that retinol pretreatment potentiates the hepatotoxicity of paracetamol. The current study is designed to investigate further this interaction in mice. To accomplish this
-
br EBV BILF A Virus Encoded
2021-04-02
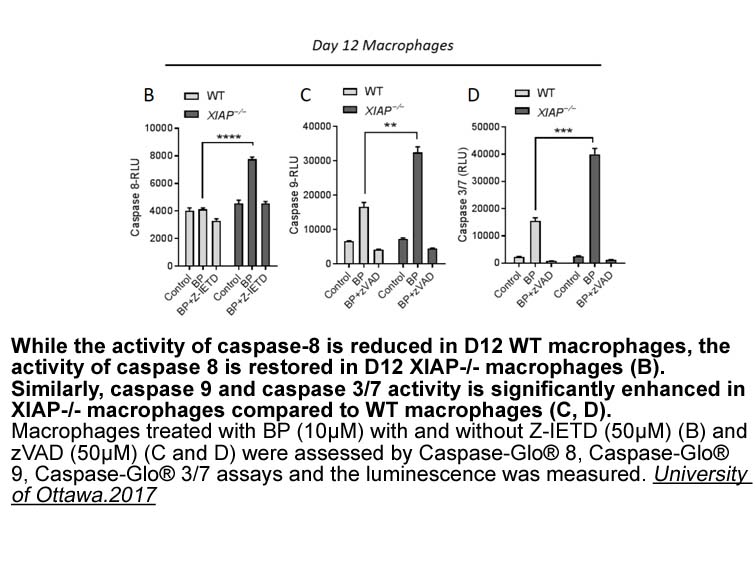
EBV-BILF1—A Virus-Encoded 7TM Receptor with Immune Evasive Functions The EBV-encoded BILF1 receptor (EBV-BILF1) is thought to be implicated in the immune evasion strategy of EBV.56, 61, 62 This orphan 7TM receptor is expressed at significant levels during the early lytic phase of the virus infect
-
CGS 21680 HCl Approximately of the etamicastat dose
2021-04-02
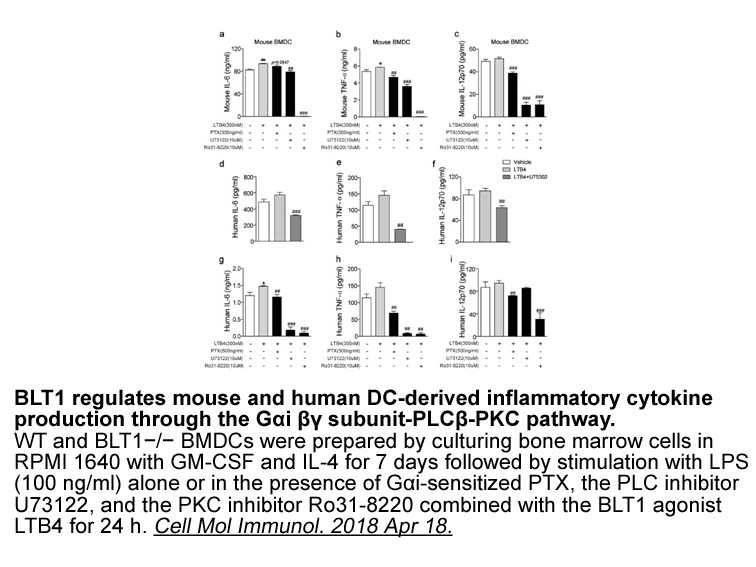
Approximately 50% of the etamicastat dose was recovered in urine, 30% in the form of etamicastat and 20% in the form of BIA 5-961. These data agree with those from a study with [14C]-labeled etamicastat in healthy subjects, which showed that approximately 95% of the administered radioactivity had be
-
In studies directed toward the development
2021-04-02
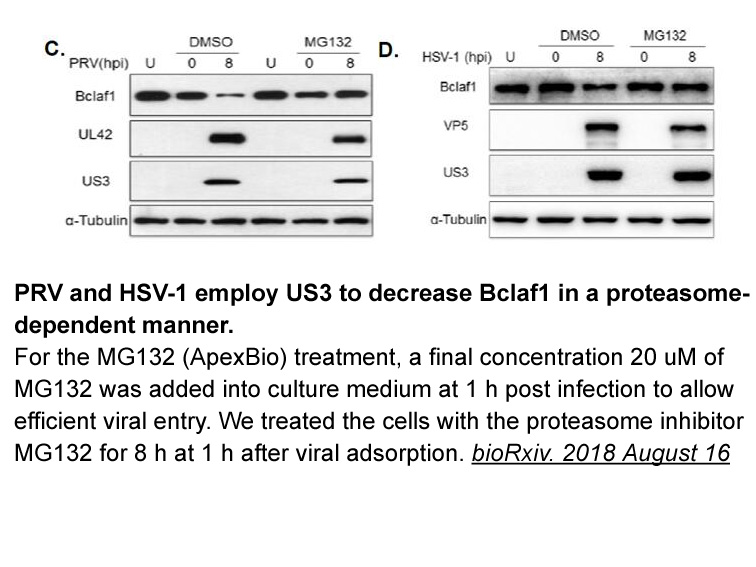
In studies directed toward the development of sequence-specific major-groove binding small Methotrexate synthesis [11], we desired a non-intercalating molecular scaffold that could direct attached moieties into the major groove. As an initial step toward this goal, we wished to study the DNA bindi
-
The objective of the present study was to
2021-04-02
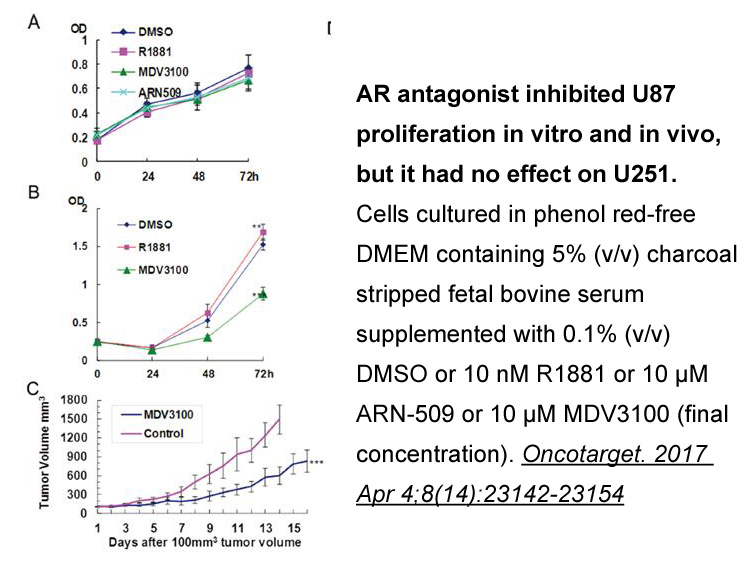
The objective of the present study was to investigate the role of the CRF system in the neuroadaptations associated with nicotine dependence. To this aim, the regulation of the gene expression of CRF and its receptors was assessed in Octreotide acetate regions belonging to the reward pathway using
-
Experiment Blunted fear potentiated startle due to deficient
2021-04-02
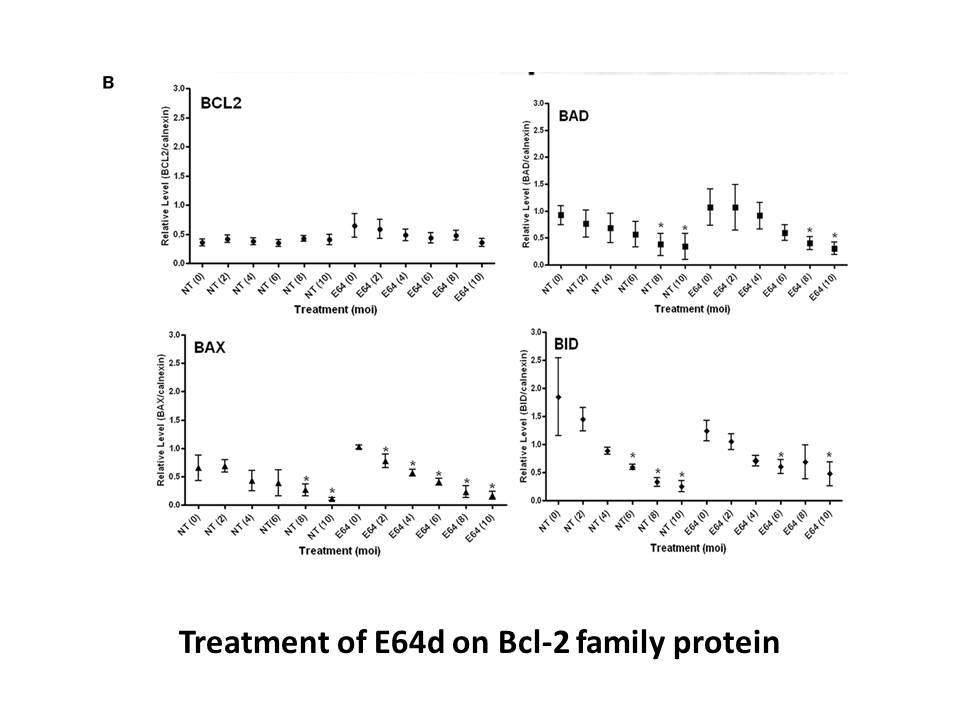
Experiment 2: Blunted fear-potentiated startle due to deficient fear acquisition. SERT+/+ and SERT+/− showed significant acquisition of the cue-shock association, whereas SERT−/− did not (trial×genotype interaction: F2,50=3.3, pand Liproxstatin-1 of fear-potentiated startle. Acquisition: Following
-
Several studies suggest that the beneficial metabolic effect
2021-04-02
Several studies suggest that the beneficial metabolic effects of adiponectin in humans are primarily mediated by its HMW isoform. Increases in the ratio of HMW to total adiponectin, but not the total adiponectin level, correlated well with improved pcpt sensitivity during treatment with the insulin
-
Other membrane currents are affected as well Some studies
2021-04-01
Other membrane currents are affected as well. Some studies have provided evidence that sulfonylureas, in addition to blocking KATP channels, also inhibit chloride and calcium channels. GLYB has been shown to almost inhibit the current generated by Na+–K+ pumps in a concentration-dependent manner (wi
16056 records 700/1071 page Previous Next First page 上5页 696697698699700 下5页 Last page